4. Mioquinas: el acoplamiento endocrino del músculo y hueso
Palabras clave:
Músculo, Hueso, Mioquinas, Sarcopenia, InflamaciónResumen
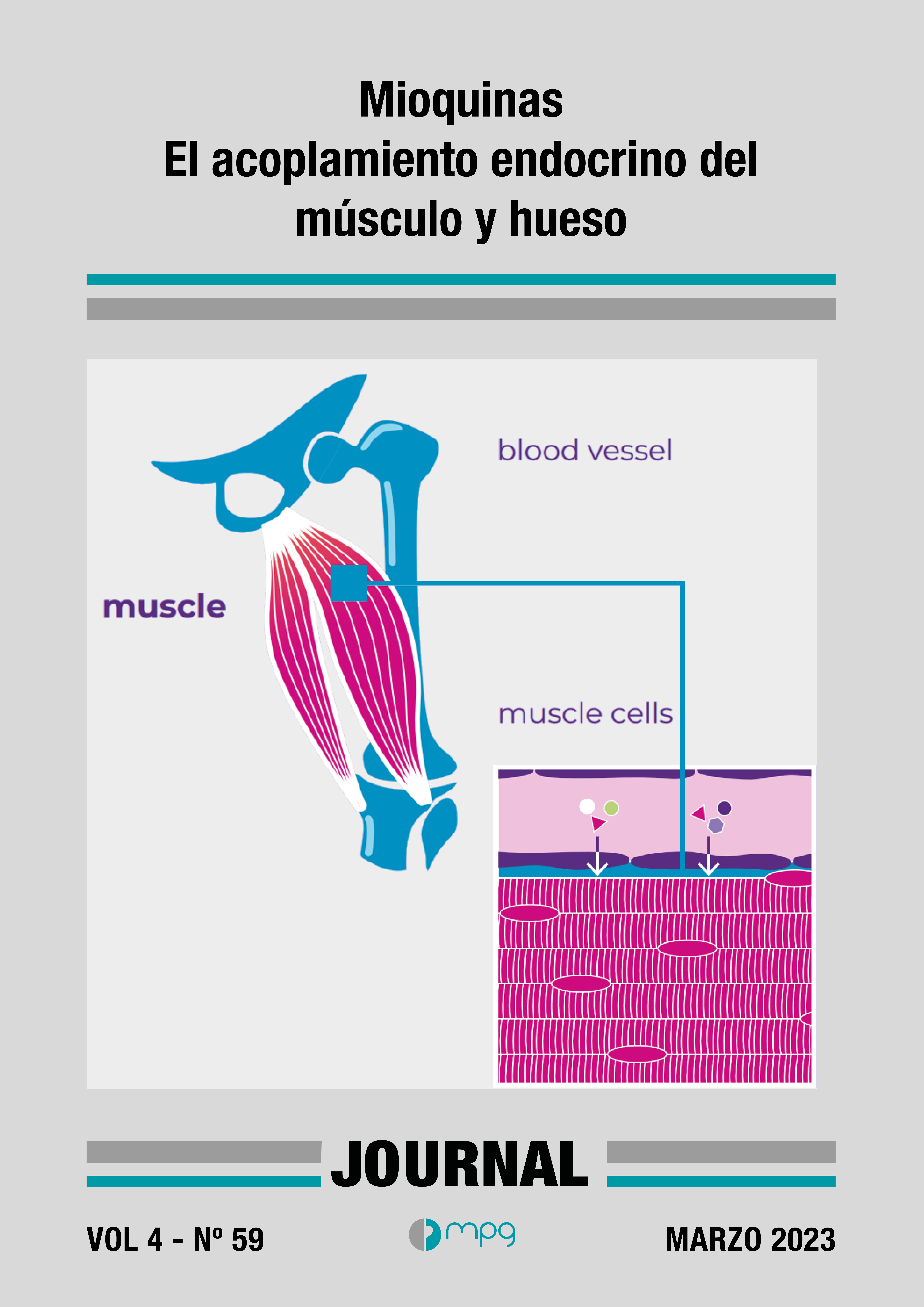
Hueso y músculo son órganos integrados y su acoplamiento se ha considerado desde un punto de vista mecánico, en el que el hueso sirve como lugar de anclaje del músculo, mientras el músculo genera carga biomecánica en el hueso y regula su metabolismo. Sin embargo, el músculo puede regular la homeostasis del hueso desde un punto de vista endocrino mediante la secreción por parte del miocito de citoquinas y proteínas llamadas mioquinas en respuesta a la contracción muscular, con efecto autocrino sobre el metabolismo del músculo y efecto paracrino/endocrino a distancia en otros tejidos como el hueso, tejido adiposo, cerebro e hígado.
En este artículo se revisa el efecto de las mioquinas inducidas por el ejercicio en la formación y resorción de hueso, así como en situaciones de inflamación crónica de bajo grado.
Bone and muscle are integrated organs and their coupling has been considered from a mechanical point of view, in which the bone serves as the anchorage site for the muscle, while the muscle generates a biomechanical load on the bone and regulates its metabolism. However, muscle can regulate bone homeostasis from an endocrine point of view through secretion by the myocyte of cytokines and proteins called myokines in response to muscle contraction, with an autocrine effect on muscle metabolism and a paracrine/endocrine effect in distant tissues such as bone, adipose tissue, brain and liver.
This article reviews the effect of exercise-induced myokines on bone formation and resorption, as well as in situations of low-grade chronic inflammation.
- Recibido: 14 Febrero 2023
- Revisión: 20 Febrero 2023
- Aceptado: 15 Marzo 2023
Referencias
Vol. 30 Nº6; págs. 13-17. 2007. V. Camozzi, A. Tossi, E. Simoni, F. Pagani, C.M. Francucci, L. Moro. Role of biochemical markers of bone remodeling in clinical practice. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.
Vol. 53 Nº3; págs. 460-484. 2017. G. Lombardi, M. Barbaro, M. Locatelli, G. Banfi. Novel bone metabolism-associated hormones: the importance of the pre-analytical phase to for understanding their physiological roles. Endocrine
Vol. 4 Nº11; págs. 797-804. 2012. A.M. Rivera-Brown, W.R. Frontera, Principles of exercise physiology: responses to acute exercise and long-term adaptations to training. PM & R. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2012.10.007
Vol. 25 Nº3; págs. 821-835. 2014. L.M. Giangregorio, A. Papaioannou, N.J. Macintyre, et al. Too Fit to Fracture: exercise recommendations for individuals with osteoporosis or osteoporotic vertebral fracture, Osteoporosis International.
Vol. 80; págs. 79-88. 2015. D.D. Bikle, C. Tahimic, W. Chang, Y. Wang, A. Philippou, E.R. Barton, Role of IGF-I signaling in muscle bone interactions. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2015.04.036
Vol. 80; págs. 115-125. S. Schnyder, C. Handschin, Skeletal muscle as an endocrine organ: PGC-1alpha, myokines and exercise. Bone. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2015.02.008
Vol. 24 Nº9; pág. 1307. 2018. L.G. Leal, M.A. Lopes, M.L. Batista Jr. Physical exercise-induced myokines and muscle-adipose tissue crosstalk: a review of current knowledge and the implications for health and metabolic diseases, Frontiers in Physiology. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01307
Vol. 24 Nº9. 2018. S. Perez-Baos, I. Prieto-Potin, J.A. Roman-Blas, O. Sanchez-Pernaute, R. Largo, G. Herrero-Beaumont. Mediators and patterns of muscle loss in chronic systemic inflammation. Frontiers in Phsysiology. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00409
Vol 14 Nº9; págs. 513-537. 2018. J.A. Batsis, D.T. Villareal. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: aetiology, epidemiology, and treatment strategies. Nature Reviews Endocrinology.
Vol. 28 Nº10; págs. 2781-2790. 2017. H.P. Hirschfeld, R. Kinsella, G. Duque, Osteosarcopenia: where bone, muscle, and fat collide, Osteoporosis International.
Vol. 21 Nº7; págs. 677-687. 2015. H. Guo, J.B. Callaway, J.P. Ting, Inflammasomes: mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nature Medicine.



MPG Journal - Política de privacidad